10 Common Diseases in Olive Trees and How To Treat Them
Olive Knowledge is a part of Amazon Associates. As an Amazon Associate, we earn from qualifying purchases. Read our Affiliate Disclosure to learn more.
Growing olive trees is very rewarding, but it is crucial to understand and remember that they are also prone to some diseases. Today, I’ll show you the 10 most common olive tree diseases and methods for treating and preventing them.
That way, you can cultivate and make this tree grow healthily and devoid of diseases.
What Causes Olive Tree Diseases?
Different diseases may plague olive trees, with each one having its own set of causes.
The usual causes of olive tree diseases are the following:
- Fungi – The presence of fungi may cause the olive tree to develop diseases. One example is verticillium wilt, which is a fungal infection/disease. Once the fungus penetrates the tree’s roots and spreads out through its entirety, it is highly likely for the branches to die. It is also possible for the affected olive tree to die in just around three years.
- Bacteria and viruses – There is also a chance for the olive tree to develop a disease brought on by the bacteria and viruses surrounding it. The problem is that once the bacteria or virus penetrates the wounds or cuts off the olive tree, the disease will aggravate or worsen. This makes it necessary to ensure that there will be no open wounds. When there is really a need to cut the tree, I highly recommend using clean tools, too.
- Climate – The climate can also contribute to the development of disease in olive trees. It becomes a problem if you move the tree to a spot or area that has an extremely different climate compared to what it was used to. Prevent the stress and disease that may come along with it by acclimating the tree first. All you have to do is change the temperature, light conditions, or anything else that will make it unique and different in a new location.
- Nutrient deficiency – If the olive tree is deficient in nutrients, especially during the stage of its growth, there is a chance that it won’t grow properly. Note that olive trees require plenty of nitrogen, which is what will support the tree’s fruiting and blooming process and its overall growth. If there are insufficient nutrients, specifically nitrogen, the leaves will begin to yellow, plus the tree may experience stunted growth.
Now that I already tackled a few of the usual causes of olive tree diseases, it is time to cover the different ailments that are truly plaguing these plants.
1. Olive Knot
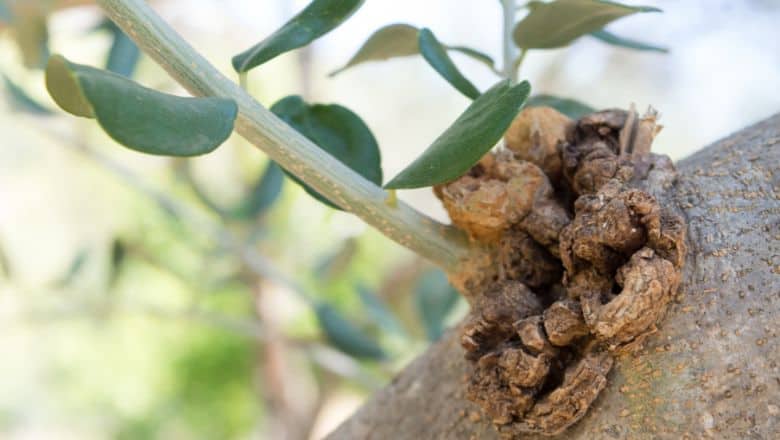

Olive knot is a disease affecting olive trees. It develops due to bacteria that may cause infections in the tree’s wound. One sign that the olive knot has already penetrated the tree is when you can see swollen parts that are around one-half to two inches.
There is also a risk of small shoots getting defoliated and eventually killed. Another noticeable sign is the reduced productivity of the tree since the olive knot ends up destroying the branches and twigs.
If you notice the infection worsening, there is a high chance of seeing the widespread weakening of the olive tree. This may also cause the olive knot to have dry branches and a substantial decrease in production.
How to treat and prevent olive knots?
One way to treat olive knots is to apply copper-containing bactericides to the affected part/s. Do this prior to the scheduled rainfall or injury.
Since you will be putting it on before the rainfall and injury, it is a major help in preventing certain ailments. Another solution is the gall eradicate paint, which can help cure affected trees.
2. Peacock spot
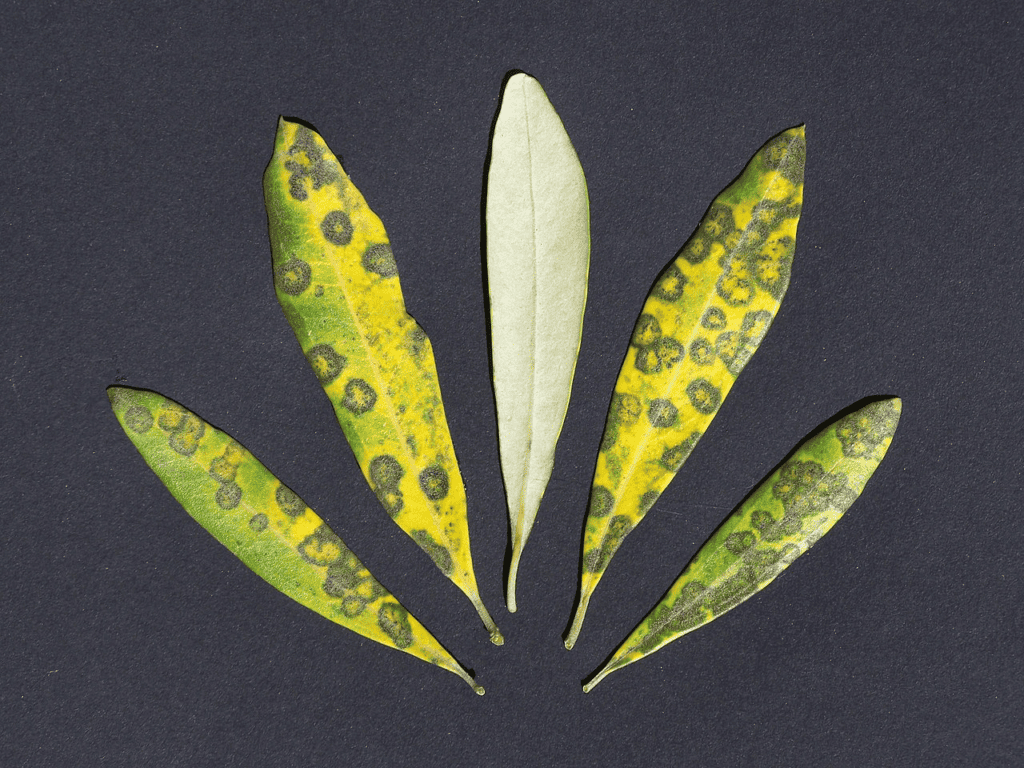

There is also what we call the peacock spot, which is known by its other name, the olive leaf spot. It is another common disease affecting olive trees when they are still in their growing season. I think it’s very easy to detect the presence of this disease since it comes in the form of small black spots that you can see atop the leaves.
I find the peacock spot problematic, though, since pests and the weather can easily and quickly spread it. This makes it kind of hard to control at times.
If left untreated, I noticed that the spot could trigger significant damage to the olives. There are even severe cases when defoliation occurs because of the spots, further resulting in the plant’s twigs dying.
How to treat and prevent peacock or olive leaf spots?
Fortunately, this disease is curable. One treatment you can use is a fungicide or a copper mixture, which you can just simply spray on the three.
You can also prevent these spots from appearing if you do the spraying during November and February. This helps in keeping the disease away.
3. Verticillium Wilt

Verticillium wilt can be classified as an olive tree disease that develops due to a soil fungus. It causes the leaves of each branch to wilt and die right after showing new growth.
Expect the affected branches to die, too, once the fungus penetrates the plant’s roots and spreads throughout the plant’s entirety. An olive tree with this disease will most likely die in just three years.
How to treat and prevent verticillium wilt?
Treating verticillium wilt is extremely difficult. In fact, a tree that’s already infected with this disease is already incurable. This is why the only thing one can do is to prevent this disease in the first place.
The olive tree has to be regularly monitored for symptoms of this disease. If the disease is still in its early stages, it helps to use a fungicide immediately. Using resistant rootstocks also helps in replanting infected groves.
4. Anthracnose
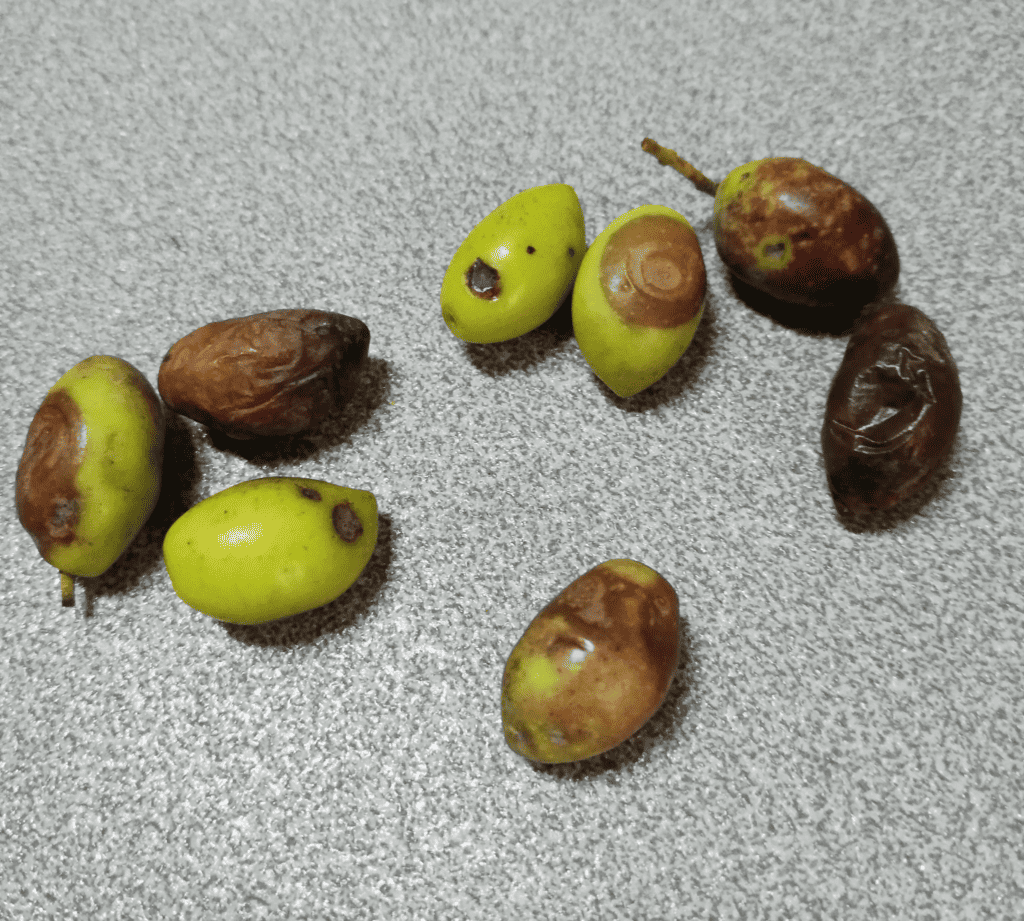

Anthracnose, otherwise called soapy olive, is now known as one of the most damaging diseases affecting olive trees. The reason is that the damage it can cause to the harvest is so significant. In fact, it can spoil the oil of any olive fruit affected by this disease.
To determine if olives have this disease, check for wrinkled and brown spots. There may also be necrotic and dry sections of the leaves that will eventually lead to them becoming completely dry. Another symptom I discovered regarding this disease is dryness in the tips of its branches.
How to treat and prevent anthracnose?
One way to prevent anthracnose from affecting olive trees is to collect and dispose of twigs and leaves. It also helps to give each branch good ventilation and proper air circulation.
This is possible if you prune infected branches and twigs during the dormant phase of the olive tree. The application of fungicide is also an effective solution to anthracnose.
5. Black Scale

Black scale can’t be classified as a disease. It is actually the primary pest that tends to affect the grove of the olive tree. When active, there is a great possibility for the pest to feed on the plant’s sap, eventually excreting sugar into the leaves.
The problem with these sugars is that they are the perfect substrates for causing sooty mold fungus to develop, further leading to a lot of damage to the plant.
How to treat and prevent the black scale?
If there is a black-scale pest infestation, the use of the correct pesticide can help stop the pests from continuously spreading. Pruning the tree regularly also helps prevent black scale from appearing in the first place.
6. Olive Fly (Bactrocera Oleae)
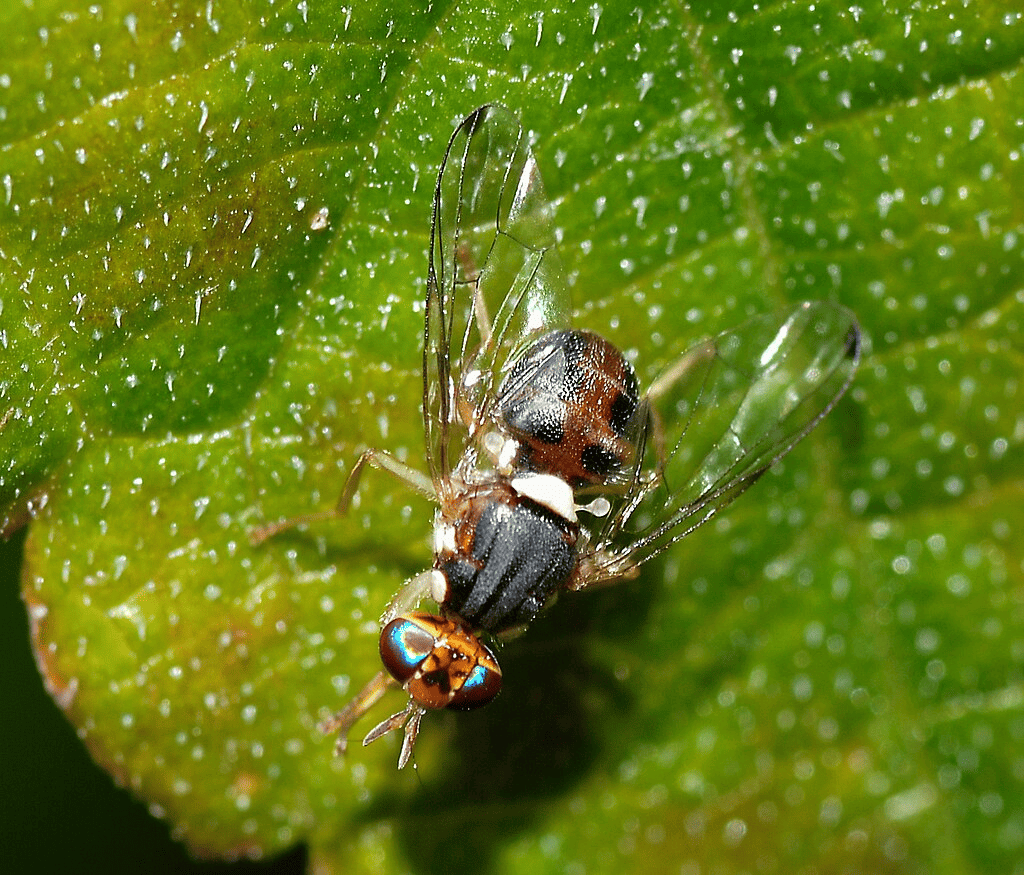
Another pest to watch out for in the olive tree is the olive fly. There is a low chance for it to kill the tree, but it is capable of wreaking havoc on the production of olives even if the conditions are favorable.
Once this pest starts laying eggs on olive fruits, they will become inedible. One sign that this is already taking place is when the olives develop tiny brown or tan entry holes.
How to treat and prevent olive flies?
An effective treatment for the olive fly is the yeast trap, which can help catch the pests attracted to the yeast. This can cause them to die in the yeast trap, thereby controlling the infestation.
In case the tree is already infected, the best solution is a trap, which contains what we call spinosad, an insecticide that can kill fruit flies and other related species. This trap is useful in monitoring olive flies or eliminating them completely.
For severe cases, applying this insecticidal trap every week is advisable until they are fully eradicated.
7. Root Rot
Olive trees are also prone to experiencing root rot. It often takes place because of excessive moisture/wetness and poor drainage. Fungicides that thrive within the soil can trigger rot.
The fact that the roots no longer feed the tree also means that its growth is also inhibited. It can also significantly reduce the growth of leaves.
How to treat and prevent root rot?
In the case of root rot, the only thing that you can do is to be extra careful in watering the tree. Check the presence of root rot by taking out the soil with the goal of exposing the roots or crown.
If there is black or brown tissue, it confirms that there is indeed a dead root. In this case, the tree is prone to dying within one to two years, so proper watering is important.
8. Botryosphaeria Canker
Another disease that may affect olive trees is Botryosphaeria canker, which is linked to insufficient rainfall for a prolonged period of time. An olive tree affected by this disease will most likely have wilting and yellowing leaves that will turn brown eventually.
As a type of canker disease, it may also lead to the loss of the tree’s primary stem or its branches. It can further result in disfigured olive trees and low-quality fruit production.
How to treat and prevent Botryosphaeria canker?
Treating Botryosphaeria canker involves the removal and disposal of dying and dead branches. Also, keep in mind that the spores often develop in the middle of the canker. With that said, the pruning should be done several inches beneath the canker of the branch and the tree infected by it.
Keep healthy trees protected by ensuring that the pruning shears and equipment used are clean and well-sanitized. Another way to treat this disease is to use a fungicide that has phosphorus acid.
9. Xylella Fastidiosa
Classified as a harmful pathogen for different plants worldwide, Xylella can be expected to infect not only olive trees but also almond, plum, and cherry trees. There is a possibility for this pathogen to spread because of insects that suck sap, like spittlebugs.
When infected, the tree can no longer move nutrients and water throughout its different parts, resulting in it withering and dying eventually. To detect this infection, watch out for signs like browning and leaf scorch. The foliage may also wilt, and the branches may wither.
How to treat and prevent Xylella fastidiosa?
The sad fact is that Xylella fastidiosa has no known cure or treatment yet. Despite that, it is still possible to prevent the disease by growing any of those Italian olive tree varieties that are known to be tolerant to Xylella.
10. Olive Fruit Moth

There is also what we call the olive fruit moth that tends to infest olive trees. This moth is a small insect that is grayish-silver in color. It has a life cycle composed of a few generations that occur in just one year. Expect this moth’s first generation to feed on olive flowers while the second eats the fruit.
The third can be expected to feed on the leaves. When an olive tree is infested with this moth, there is a high chance for all its flowers to get destroyed. You will also notice the sudden weakening of the tree and the dropping of its fruits prematurely.
There is also a high chance that the pest is already present if one observes at least three punctures in each branch. If these signs are visible, it is crucial to take action to get rid of the moth immediately.
How to treat and prevent olive fruit moths?
The best solution for olive fruit moths is the insecticidal moth. It can help control these insects in the same way as the hot summer temperature does.
Bottom Line
Based on what we have covered, it is safe to say that there are indeed several olive tree diseases that anyone who wishes to grow this tree should monitor. Despite the pests and diseases that may inflict olive trees, there is no reason not to make it a part of one’s garden or backyard.
With proper care and regular monitoring, pests and diseases can be prevented. It also helps to be knowledgeable about their possible solutions and treatments so it is easy to act on them appropriately once signs and symptoms occur.
